Blogs
2025.06.04
What is the gradient? (Applications of Separate type clinometer)
What do you think of when you hear the word “ gradient”? I’m sure some of you may be thinking of hills, mountain slopes, roof angles, etc.



According to Kojien, Japan’s national [Japanese + encyclopedia] dictionary, “‘gradient’ means ‘the degree of inclination of a sloping surface. It is usually interpreted as “the ratio of the distance from the horizontal plane to the horizontal variation of the inclined plane.” It is interpreted as follows.
In everyday use, “lukewarm gradient” is used when the gradient is slow or judgmental. Conversely, “the gradient is fast” is used when the gradient is steep or judgment is quick. It is interesting to note that “lukewarm” is used not only to describe a loose slope and “quick” to describe a steep slope, but also to express the quickness of a person’s judgment.
In fact, there is a unit of measure for this “gradient” and a measuring instrument to measure it!
First, let’s talk about units. There are percent (%), per mil (‰), degrees (°), and fractions (ratio). Percentage is the ratio of how much it is when the whole of the standard is considered to be 100, and per mil is the ratio of how much it is when the whole of the standard is considered to be 1000. Degrees represent the angle of inclination from a horizontal plane, and fractions are the ratio of the vertical distance to the horizontal distance.
- Percentage (%): A slope of 10% is defined as a slope that rises 10 cm for every 100 cm of travel.
- Permil (‰): A gradient of 2‰ is defined as a rise of 2 meters for every 1000 meters.
- Degrees (°): The angle of inclination from the horizontal plane expressed in degrees.
- Fraction (ratio): The ratio of the vertical distance to the horizontal distance. For example, 1:2 or 1/2.
- Sun gradient: A Japanese roof gradient is the vertical distance to a horizontal distance of 1 shaku (30.3 cm) expressed in “sun” (1/10 shaku = 3.03 cm). For example, a 4-sun gradient means that a 1-shaku advance raises the roof by 4 sun (12.1 cm).
Gradient is expressed in various units, but it is mainly easy to understand by considering how much the vertical distance is in relation to the horizontal distance (ratio of horizontal distance to vertical distance).
The unit of the tilt angle, the degree (°), is considered in terms of tangent (tan), one of the trigonometric functions in mathematics; if Θ is the angle you want to find, tanθ=vertical distance/horizontal distance, so you can find it by calculating Θ=tan-1 vertical distance/horizontal distance. It may be a little complicated when talking about mathematics, but if you are interested, you can calculate the vertical distance/horizontal distance with a function calculator and press the tan-1 button with the value displayed to obtain the slope angle, so if you are interested, please try it. Also, if you search for “ gradient calculation” or “gradient conversion table” on the Web, you will find sites that introduce automatic calculation tools and conversion tables, so you may want to look at those places as well.
Next, we will discuss “gradient meters,” measuring instruments that can measure gradient.
We have a “Drainpipe Gradient Measuring clinometer” manufactured by applying the Separate type clinometer, which is part of our product lineup, and we will explain it there. For details, please see the product description page. (Please click here for Drainpipe Gradient Measuring Clinometer!)
This drainpipe gradient measuring clinometer is designed to measure the gradient of drainpipes installed in inaccessible high locations such as ceilings. Measurement can be easily made by simply placing the sensor of the instrument on the drain pipe.
Actual measurements and results are shown below.
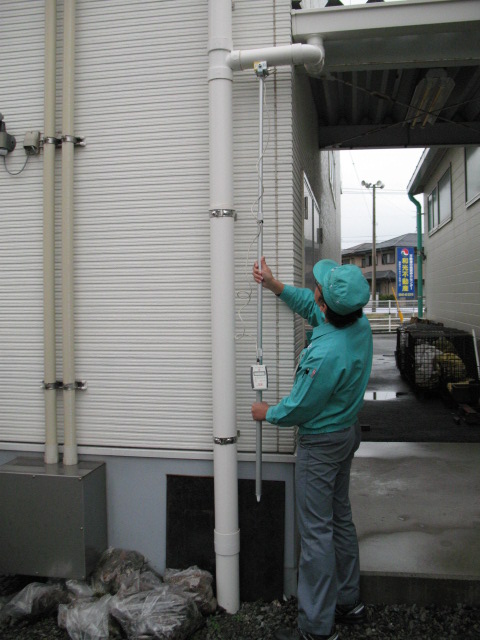
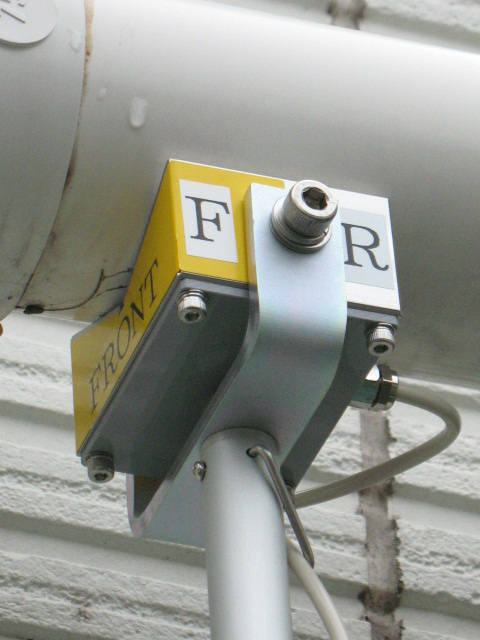
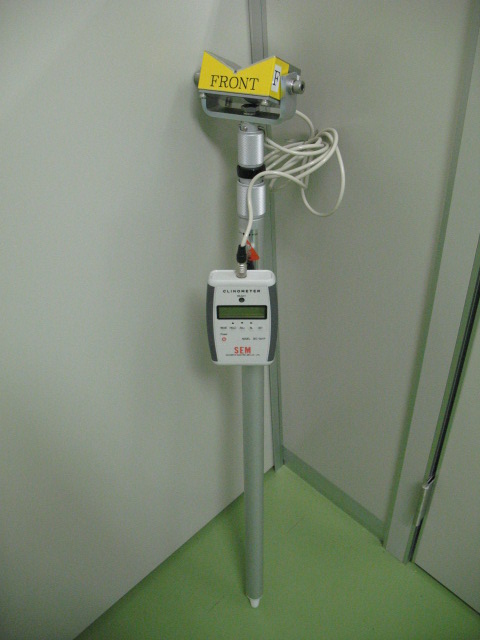



When the sensor is pressed against the drainpipe, the measurement results are
FRONT ◢ REAR is indicated. This indicates a downward slope from the REAR side of the V-block sensor toward the FRONT side, with a value of 2.4/100. This is indicated in the 100 fraction I mentioned in the units section above, and indicates a “2.4% gradient”. In other words, when the horizontal distance is 100%, the vertical distance is 2.4%. For example, if the horizontal distance of a drainpipe is 100 cm, the vertical distance is 2.4 cm. Converted to an angle, this is approximately 1.37°. Although it may seem small when looking at the numbers only, according to the Building Standard Law, the standard slope is generally 2%, which means that the standard has been met.
So far, we have talked about the word “ gradient,” its units, and its measurement. We hope that you are now interested in gradient, inclination, and our measuring instruments that can measure them.
[Related products]
- SEC-S011F-H Separate type clinometer (Horizontal measurement type)
- SEC-S011F-V Separate type clinometer (Vertical measurement type)
- SEC-021FivⅡ-H Inclination angle monitoring system
- SEC-S011F-P Drainpipe Gradient Measuring Clinometer

