Blogs
2026.01.19
Curious about the Hardness of Wood? – About a Wood Strength Evaluation Device –
This time, instead of continuing with the digital levels we have introduced so far, I would like to shift focus slightly and talk about wood.
When you hear the word “wood,” what comes to mind? In nature, you might think of mountains and forests; in the workplace, logging or lumber processing; and in everyday life, wooden buildings or playground equipment in parks.



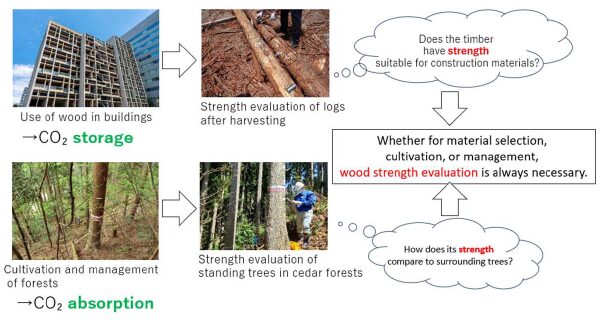
In recent years, growing concern for the environment has brought increased attention to efforts toward decarbonization, often referred to as carbon neutrality—the concept of balancing CO₂ emissions with CO₂ absorption.

As part of these initiatives, the use of wood in buildings, along with forest cultivation and management, is being promoted. By using wood in construction, CO₂ can be stored within buildings, while forest cultivation and proper management contribute to increased CO₂ absorption. Naturally, wood used in buildings must have high strength (hardness). Likewise, in forest cultivation and management, “strength (hardness)” is considered an important indicator for evaluating the growth and quality of trees. In other words, the need to measure wood hardness—that is, to evaluate wood strength—is steadily increasing.
At our company, we are currently developing a handheld device for evaluating the strength of wood. This development traces back to a five-year research project (starting in 2016) sponsored by Japan’s Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, in which five organizations, including ours, collaborated on developing forestry machinery capable of automatically assessing wood strength and enabling the production of high-quality timber. Our role in this project was to equip the head section of the forestry machine (the harvester—the orange-colored part) with a measuring device to evaluate wood strength.

(overall view)

As for how wood strength is determined, it can be expressed using Young’s modulus. This value can be calculated from the speed of sound traveling through the wood and the material’s density, based on a specific relationship.
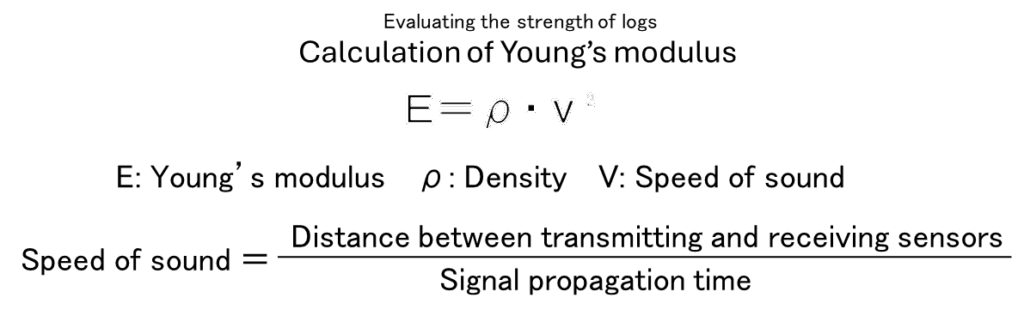
Our measuring device uses sensors equipped with piezoelectric elements, which are attached to the wood to transmit and receive signals (sound waves) and measure their propagation time. The distance between the sensors is measured before installation, so the signal propagation distance is known. By dividing the distance by the measured time, the propagation speed (speed of sound) within the wood can be calculated. These calculations are performed within the device and displayed on the screen. Additionally, since density information is required to determine strength (Young’s modulus), either measured values or representative (estimated) values can be entered into the device, and the calculated results are then displayed.
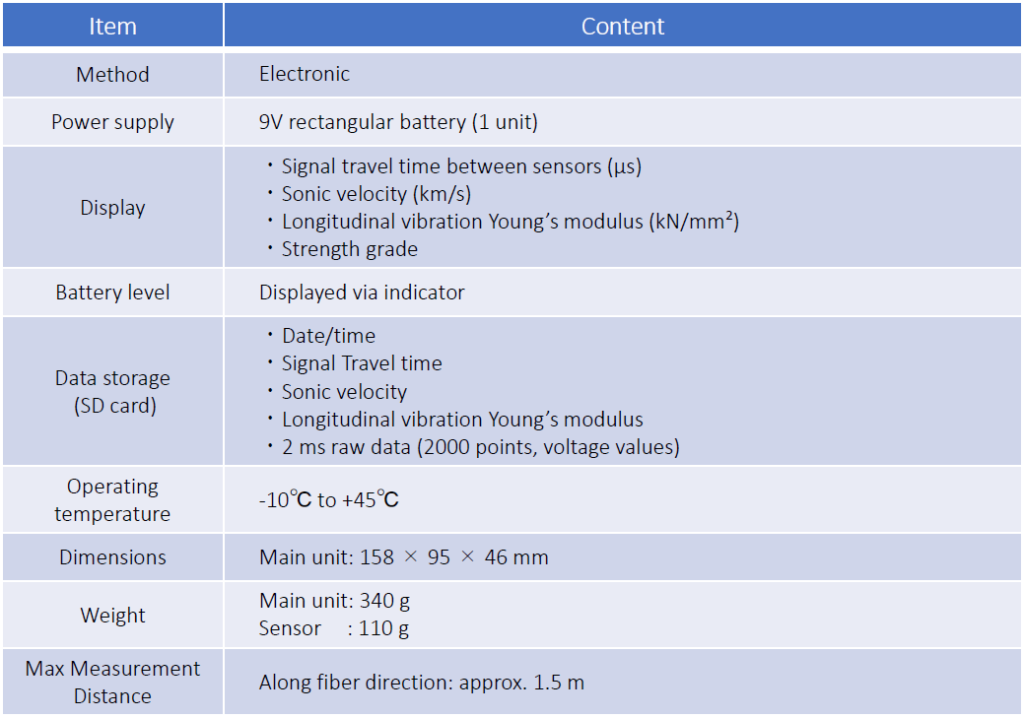
Development is still ongoing, but the current proposed specifications are shown below.
So far, we have introduced our wood strength evaluation device—what did you think? We hope this article serves as an opportunity to deepen your interest in wood materials and environmental issues.

